How Antigen Testing Works
The Lifecycle of COVID-19
To understand how COVID-19 testing works, we first have to understand “virus kinetics,” the model used to describe the lifecycle of the virus within an infected individual and for how long that person remains infectious.
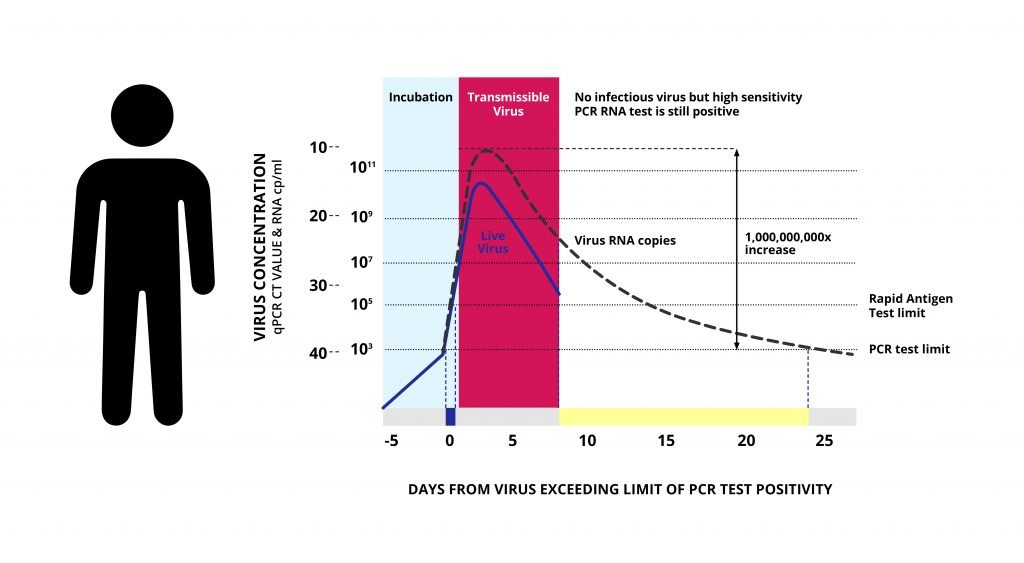
The above chart plots the life cycle of the SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19) virus, breaking it down into three parts. First, the virus incubation period is usually the first 4 days after contracting the virus. During this time, the virus is not “live” and individuals are not contagious. Second, the transmissible period occurs between around days 5-11. During this time, the virus is “live” and individuals are contagious and should self-isolate or seek medical attention if conditions worsen. The third period is the post-recovery period at about and after day 11 when the virus is no longer transmissible. However, the virus RNA copies can stay in the body for up to 15 days after this period.
The Difference Between Antigen and PCR Tests*
As virus kinetics shows, “infected” does not mean “infectious.” In other words, having the virus doesn’t necessarily mean that you are contagious but, rather, depends on the viral load. An infected individual is usually only infectious for 5-7 days when the viral load in the body is high.
Antigen tests detect proteins specific to COVID-19, which are present in large amounts when the person is infectious and has a high viral load. Antigen tests are not a diagnostic tool but were designed to determine whether or not a person is infectious and can transmit the disease. Antigen tests can detect the virus as early as 2-3 days after infection but will not yield a positive result in individuals who have passed the transmissible stage.
In contrast, PCR tests, represented by the “high sensitivity” line on the graph, detect the viral RNA, which exists long after a person passes the transmissible period. While PCR tests can detect the virus before the transmissible period and also in asymptomatic individuals, it can also yield a positive result in patients who have already recovered and are no longer infectious, barring them from returning to work or school for as much as 15 days longer than necessary.
Practical Application
Antigen tests display results within 20-30 minutes and don’t require the use of special equipment. There have been numerous cases of asymptomatic patients infecting others while waiting for their test results. Had those patients taken an antigen test, they would have been removed from circulation immediately.
***The Innova rapid antigen test is currently not for sale in the USA***
Summary
Antigen tests determine if a person is infectious and is a much more effective screening tool. With regular testing (daily or 3 times a week) infectious individuals can be quickly identified and removed from circulation. Antigen tests are a powerful tool to suppress the infection rate without forcing unnecessary self-isolation and entire cities to go into lockdown. With frequent antigen testing, businesses can stay open, students can go back to school, and everyone can enjoy greater peace of mind.
